Entities
An entity is an object that is persistent in a scene (e.g., nodes, assets) or across scenes (e.g., plugins). Scripting in Warudo is all about defining your own entity types and interacting with the Warudo runtime. You can define your own entity type by inheriting a base class provided by Warudo:
- Node: Inherit from
Nodeto create a new node type. A node type can define data inputs, data outputs, flow inputs, flow outputs, and triggers. A node is instantiated by dragging it from the node palette to the blueprint editor; the node instance is saved along with the blueprint. - Asset: Inherit from
Assetto create a new asset type. An asset type can define data inputs and triggers. An asset is instantiated by using the Add Asset menu; the asset instance is saved along with the scene. - Plugin: Inherit from
Pluginto create a new plugin type. A plugin type can define data inputs and triggers. A plugin is loaded when Warudo starts, or when the plugin is hot-reloaded. There is only one plugin instance per plugin type, and data inputs are saved across scenes. - Structured Data: Inherit from
StructuredDatato create a new structured data type. Structured data is a complex data type that can be used as an "embedded" data input in nodes, assets, or plugins.
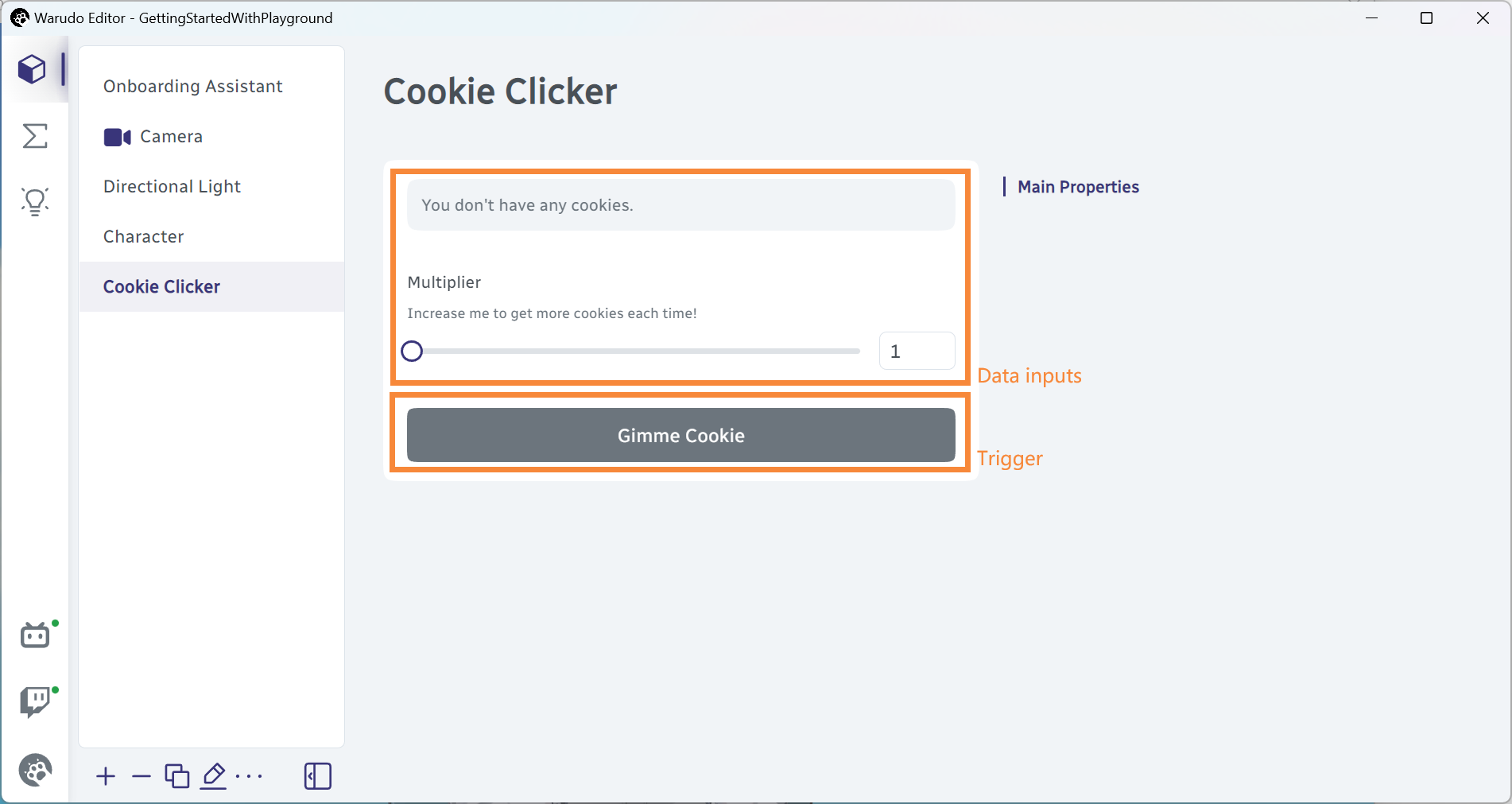
In the Creating Your First Script tutorial, we created a custom node type called HelloWorldNode and a custom asset type called CookieClickerAsset.
The concept of entities is loosely similar to Unity's MonoBehaviour, but with a more structured approach.
After an entity is instantiated, it is automatically assigned a UUID (unique identifier) by Warudo. You can access it via the Id property. This UUID is then used to identify the entity in the scene, and is saved along with the scene.
An entity type can contain regular C# fields and methods. However, to interface with the Warudo runtime, you need to create ports and triggers in the entity. All entities can have data input ports and triggers, while nodes can additionally have data output ports, flow input ports, and flow output ports.
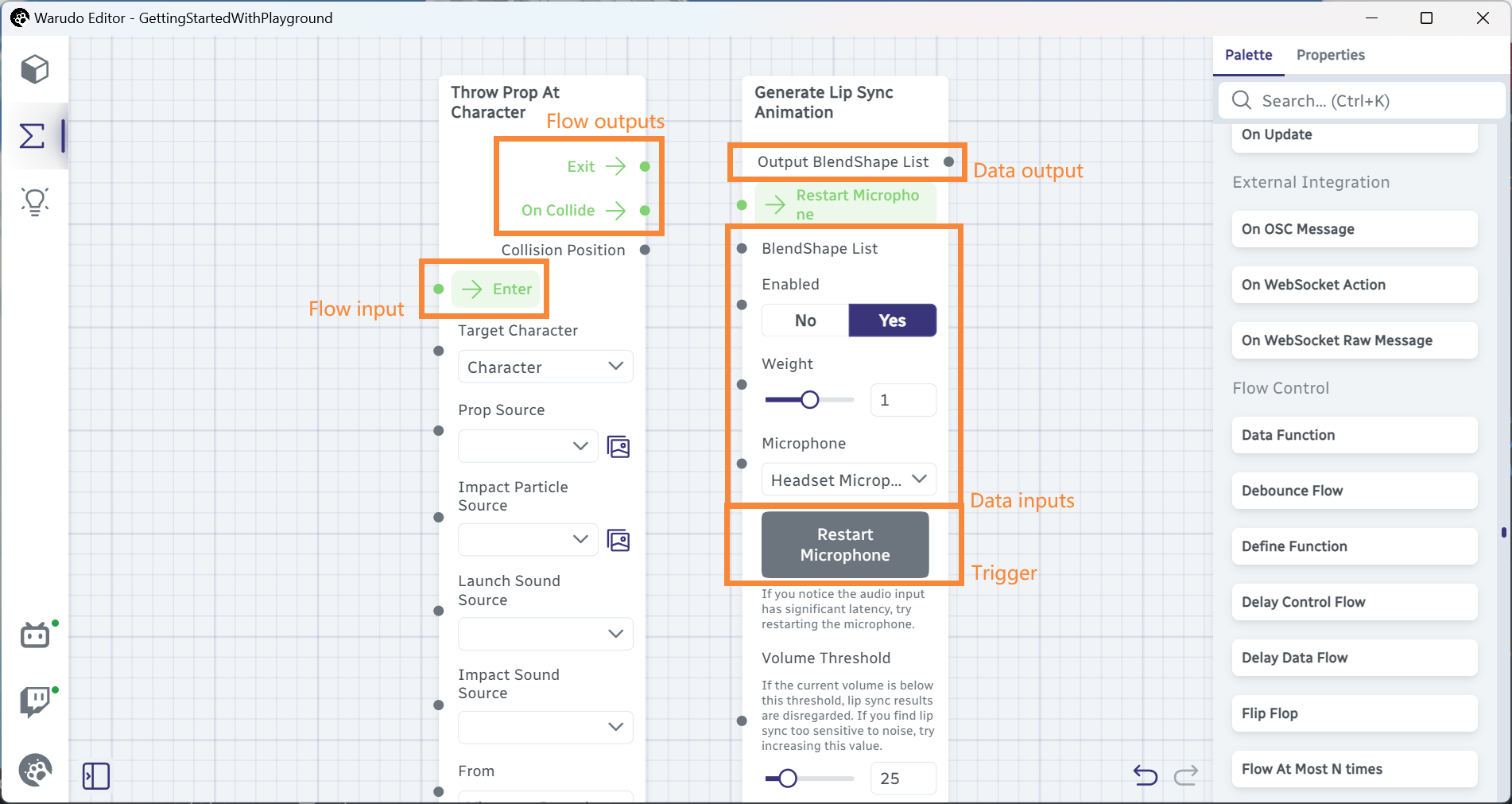
Lifecycle
An entity has a lifecycle that consists of several stages:
OnCreate(): Called when the entity is created. This is where you should initialize the instance fields, subscribe to events, etc.- Assets: Called when a new asset is added to the scene by the user, or when the scene is loaded.
- Nodes: Called when a new node is added to the blueprint by the user, or when the scene is loaded. Nodes are always created after assets.
- Plugins: Called when the plugin is loaded by Warudo on startup, or when the plugin is hot-reloaded.
- Structured Data: Called when the parent entity is created, or when the user adds a new structured data to an array of structured data.
OnDestroy(): Called when the entity is destroyed. This is where you should release resources, etc.- Assets: Called when the asset is removed from the scene by the user, or when the scene is unloaded.
- Nodes: Called when the node is removed from the blueprint by the user, or when the scene is unloaded. Nodes are always destroyed after assets.
Deserialize(TSerialized data): Called when the entity is deserialized from a saved state. For example, this method is called on an asset when the scene is just opened and loaded. You usually do not need to override this method.Serialize(): Called when the entity needs to be serialized to a saved state. For example, this method is called on an asset when the scene is about to be saved, or need to be sent to the editor. You usually do not need to override this method.
Assets, nodes, and plugins have extra lifecycle stages:
OnUpdate(): Called every frame when the entity is not destroyed. This is similar to Unity'sUpdate()method.OnPreUpdate()andOnPostUpdate()are also provided. They are called before and afterOnUpdate(), respectively.
OnLateUpdate(): Called every frame afterOnUpdate(). This is similar to Unity'sLateUpdate()method.OnFixedUpdate(): Called every fixed frame. This is similar to Unity'sFixedUpdate()method.OnEndOfFrame(): Called at the end of the frame. This is similar to using Unity'sWaitForEndOfFramecoroutine.OnDrawGizmos(): Called when the entity should draw gizmos. This is similar to Unity'sOnDrawGizmos()method.
The update order is as follows: plugins → assets → nodes.
You can override these lifecycle methods to implement custom behavior for your entities. For example, if you want to run something on every frame, override the OnUpdate() method.